LCP Client
Overview
LCP Clientは、ELCが生成した状態遷移や状態の存在証明を示すコミットメントをon-chainで検証するLight Clientである。
これは、ibc-goやibc-solidityのLight Client moduleとして実装されることを想定しており、ICS-02に準拠する。検証対象のUpstream chainごとにDownstream chain上にそのインスタンスを作成する必要がある。
Desired Properties
LCP Clientは、LCPのセキュリティモデルに基づき以下の性質を満たさなければならない:
- LCP Clientは、ELCにより生成された
UpdateStateProxyMessageを検証することで正しくUpstream chainの状態を追跡する。例えば、悪意あるLCP operatorにより異なる構成のELCに基づくメッセージおよびコミットメントが提供された場合、LCP Clientはそれを拒否する。 - SGX危殆化のリスクを軽減するため、RAに得られたEKは、RAのtimestampを基準とした有効期限を持つべきであり、その有効期限を過ぎたEKによるコミットメントは拒否される。
State definition
ClientState
ClientState定義は次のようになる:
message ClientState {
bytes mrenclave = 1;
uint64 key_expiration = 2;
bool frozen = 3;
Height latest_height = 4;
// e.g. SW_HARDENING_NEEDED, CONFIGURATION_AND_SW_HARDENING_NEEDED (except "OK")
repeated string allowed_quote_statuses = 5;
// e.g. INTEL-SA-XXXXX
repeated string allowed_advisory_ids = 6;
repeated bytes operators = 7;
uint64 operators_nonce = 8;
uint64 operators_threshold_numerator = 9;
uint64 operators_threshold_denominator = 10;
}
mrenclaveはこのLCP Clientに対応するLCP EnclaveのMRENCLAVEを示す。例えば、LCP ClientがEthereum上にデプロイされ、Tendermint chainを参照する場合、このMRENCLAVEはTendermint ELCを含むLCP EnclaveのMRENCLAVEと一致する必要がある。key_expirationはAVRに含まれるEKの有効期限を示す(RAのtimestampを基準とした秒数)frozenはこのclientが凍結されているかどうかを示すlatest_heightはこのclientが検証済みのELCの最新の高さを示す。0の場合、ClientStateは初期化が完了していないことを示す。allowed_quote_statusesは許容されるAVRのquote statusのリストを示すallowed_advisory_idsは許容されるAVRのadvisory idのリストを示す- (optional)
operatorsはこのclientに対応するLCP Operatorのアドレスのリストを示す。 - (optional)
operators_nonceはこのClientに対応するLCPのoperatorのnonceを示す - (optional)
operators_threshold_numerator,operators_threshold_denominatorはこのClientStateに対応するELCのoperatorのthresholdを示す
また、ClientStateに基づいて検証されたEKのリストは以下のように定義されるAuxStorageに保存される:
message AuxStorage {
// key: EKAddr
map<bytes, EKInfo> ekInfos = 1;
}
message EKInfo {
uint64 expired_at = 1;
bytes operator;
}
ekInfosはEKAddrをkeyとし、そのEKの有効期限とEKの所有者であるoperatorを示すEKInfoをvalueとするmapである。operatorは20バイトの値であり、0の場合はoperatorが未設定であることを示す。
ConsensusState
ConsensusStateは高さ(i.e., consensus height)ごとのELCの状態を示す。その定義は次のようになる:
message ConsensusState {
bytes state_id = 1;
// unix timestamp in seconds
uint64 timestamp = 2;
}
state_idはconsensus heightに対応するELCのState IDを示すtimestampはconsensus heightに対応するUpstream chainのブロックのtimestampを示す
LCP Operator
LCP Operator(単にOperator)はLCP Nodeを運用するオペレータを指す。Operatorは自身のEOAの秘密鍵を保有し、それらの公開鍵をLCP ClientのClientStateのoperatorsにセットすることで、そのClientを用いたコミットメントの検証時に追加でこれらのOperatorの署名を要求することができる。この閾値はoperators_threshold_numerator, operators_threshold_denominatorより定められる。ただし、これはオプションであり、ClientStateのoperatorsが空の場合は追加の署名を要求しない。
operatorsが空ではない場合、UpdateOperators関数によりOperatorの追加、削除、および閾値の変更が可能である。
Storage
関数におけるSTORAGEは、LCP ClientのClientState, ConsensusState, およびAuxStorageを保持するための永続的なストレージを示す。このストレージは、Ethereumのストレージと同様の永続性を持ち、LCP Clientによってのみ制御が可能でなければならない。
STORAGEは以下のような構造を持つ
struct ClientStorage {
ClientState clientState;
mapping(Height => ConsensusState) consensusStates;
AuxStorage aux;
}
mapping(string clientId => ClientStorage) STORAGE;
Functions
CreateClient
CreateClientは、ClientState, ConsensusStateを与えてLCP Clientの新しいインスタンスを作成するための関数である。通常、この関数はIBC handlerを介してRelayerにより呼び出される。
ibc-solidityにおいては、CreateClient中に与えられた状態を以下の関数により検証する。
function initializeClient(
string calldata clientId,
ClientState calldata clientState,
ConsensusState calldata consensusState
) public returns (Height memory height) {
require(clientState.latest_height.revision_number == 0 && clientState.latest_height.revision_height == 0);
require(!clientState.frozen);
require(clientState.key_expiration != 0);
require(clientState.mrenclave.length == 32);
require(clientState.operators_nonce == 0);
require(
clientState.operators.length == 0
|| (clientState.operators_threshold_numerator != 0 && clientState.operators_threshold_denominator != 0)
);
require(clientState.operators_threshold_numerator <= clientState.operators_threshold_denominator);
require(consensusState.timestamp == 0);
require(consensusState.state_id.length == 0);
// ensure the operators are sorted(ascending order) and unique
address prev;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < clientState.operators.length; i++) {
require(clientState.operators[i].length == 20, "invalid operator address length");
address addr = address(bytes20(clientState.operators[i]));
require(addr != address(0), "invalid operator address");
require(prev == address(0) || prev < addr, "invalid operator address order");
prev = addr;
}
STORAGE[clientId].clientState = clientState;
return clientState.latest_height;
}
RegisterEnclaveKey
RegisterEnclaveKeyは、LCPが生成したEnclave Key(EK)をClientに登録するための関数である。1つのLCP Clientにつき、複数のEKを登録することができる。
この関数は次のように定義される:
struct RegisterEnclaveKeyMessage {
bytes report;
bytes signature;
bytes signing_cert;
// optional
bytes operator_signature;
}
function registerEnclaveKey(string calldata clientId, RegisterEnclaveKeyMessage calldata message)
public
returns (Height[] memory heights)
{
require(verifyAVR(
message.report, message.signature, message.signing_cert,
STORAGE[clientId].clientState.allowed_quote_statuses,
STORAGE[clientId].clientState.allowed_advisory_ids
), "invalid AVR");
(bytes32 mrenclave, uint64 attestationTime, address enclaveKey, address operator) = extractAVRInfo(message.report);
require(bytes32(STORAGE[clientId].clientState.mrenclave) == mrenclave, "unexpected mrenclave");
// if `operator_signature` is empty, the operator address is zero
address signer;
if (message.operator_signature.length != 0) {
signer = verifyECDSASignature(
keccak256(LCPOperator.computeEIP712RegisterEnclaveKey(message.report)), message.operator_signature
);
}
require(operator == address(0) || operator == signer, "unexpected operator");
uint64 expiredAt = attestationTime + STORAGE[clientId].clientState.key_expiration;
require(expiredAt > block.timestamp, "AVR already expired");
EKInfo storage ekInfo = STORAGE[clientId].aux.ekInfos[enclaveKey];
if (ekInfo.expiredAt != 0) {
require(ekInfo.operator == operator, "unexpected operator");
require(ekInfo.expiredAt == expiredAt, "unexpected expiredAt");
// NOTE: if the key already exists, don't update any state
return heights;
}
ekInfo.expiredAt = expiredAt;
ekInfo.operator = operator;
emit RegisteredEnclaveKey(clientId, enclaveKey, expiredAt, operator);
// Note: client and consensus state are not always updated in registerEnclaveKey
return heights;
}
registerEnclaveKey関数は、Attestation Serviceにより得られたVerifiable Quote(IASにおいてはAVRとその署名)を要求し、その検証を行い成功した場合にAVRのQuoteのreport dataに含まれるEKAddrを有効期限やOperator addressとともにekInfosにセットする。
検証は、IASの場合は以下の通り:
- IASにより得られたAVRに対するIntelの署名の検証
- AVRに含まれるisvEnclaveQuoteStatusやadvisoryIDの値がClientStateの許容する値であることを確認する。
- AVRに含まれるQuoteのMRENCLAVEがClientStateのMRENCLAVEと一致することの確認
- AVRのtimestampとClientStateのkey_expirationを加算した値が現在時刻より未来であることの確認
- AVRのQuoteのreport dataにoperator addressが含まれる場合は以下の検証を行う。含まれない場合は、
ekInfosのopeartor fieldに0をセットする: 5-1. そのoperator addressと対応する鍵によるreportに対する有効なoperator_signatureが含まれることの確認 5-2. operator addressをekInfosにセットする
UpdateClient
UpdateClientは、ELCの状態遷移を示すメッセージを元にLCP Clientの指定されたClient IDに対応するClientStateとConsensusStateを更新する関数である。この関数は、IBC handlerを介してRelayerにより呼び出される。
この関数は次のように定義される:
struct UpdateClientMessage {
// abi.encode(HeaderedProxyMessage)
bytes proxy_message;
bytes[] signatures;
}
struct HeaderedProxyMessage {
// LCP_MESSAGE_HEADER_UPDATE_STATE: bytes32(uint256(LCP_MESSAGE_VERSION) << 240 | uint256(LCP_MESSAGE_TYPE_UPDATE_STATE) << 224)
// LCP_MESSAGE_HEADER_MISBEHAVIOUR: bytes32(uint256(LCP_MESSAGE_VERSION) << 240 | uint256(LCP_MESSAGE_TYPE_MISBEHAVIOUR) << 224)
bytes32 header;
bytes message;
}
function updateClient(string calldata clientId, UpdateClientMessage.Data calldata message)
public
returns (Height.Data[] memory heights)
{
verifySignatures(clientId, keccak256(message.proxy_message), message.signatures);
HeaderedProxyMessage memory hm =
abi.decode(message.proxy_message, (HeaderedProxyMessage));
if (hm.header == LCP_MESSAGE_HEADER_UPDATE_STATE) {
return updateState(clientId, abi.decode(hm.message, (UpdateStateProxyMessage)));
} else if (hm.header == LCP_MESSAGE_HEADER_MISBEHAVIOUR) {
return submitMisbehaviour(clientId, abi.decode(hm.message, (MisbehaviourProxyMessage)));
} else {
revert("unexpected header");
}
}
この関数はproxy_messageに対して有効なsignaturesであることを検証した上で、デコードして得られたHeaderに応じてそれぞれ異なる関数を呼び出す。現在、次の2種類のメッセージをサポートする:
UpdateStateProxyMessage: 2つの高さに対応するELCの状態遷移を示すMisbehaviourProxyMessage: ELCが検知したChainのmisbehaviourを示す
EKによる署名の検証は、以下の関数verifySignaturesで行われる。
function verifySignatures(string calldata clientId, bytes32 commitment, bytes[] memory signatures)
internal
view
{
uint256 opNum = STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators.length;
if (opNum == 0) {
require(signatures.length == 1, "invalid signatures length");
ensureActiveKey(clientId, verifyECDSASignature(commitment, signatures[0]), address(0));
} else {
require(signatures.length == opNum, "invalid signatures length");
uint256 success = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < signatures.length; i++) {
if (sig.length != 0) {
ensureActiveKey(
clientId,
verifyECDSASignature(commitment, signatures[i]),
address(bytes20(STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators[i]))
);
success++;
}
}
require(success * STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators_threshold_denominator >= STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators_threshold_numerator * opNum, "insufficient signatures");
}
}
function ensureActiveKey(string calldata clientId, address ekAddr, address opAddr) internal view {
EKInfo storage ekInfo = STORAGE[clientId].ekInfos[ekAddr];
uint256 expiredAt = ekInfo.expiredAt;
require(expiredAt != 0, "enclave key not exist");
require(expiredAt > block.timestamp, "enclave key expired");
require(opAddr == address(0) || ekInfo.operator == opAddr, "unexpected operator");
}
この関数は、メッセージに対する署名を以下のように検証する:
- ClientStateの
operatorsを空の場合、1つの署名だけを検証し、そのEKがactiveであることを確認する - ClientStateの
operatorsが空でない場合、以下の検証を行う:- ClientStateの
operatorsの数とsignaturesの数が一致することを確認する - 各署名に対して、空ではない場合は署名が有効であることとそのEKがactiveであることを確認し、また署名のインデックス
iについてekInfos[i].operatorがoperators[i]と一致することを確認する - EKが対応するoperatorであることを確認する
- 上記の検証に成功した署名の数が閾値を超えていることを確認する
- ClientStateの
UpdateState
この関数は、ELCが生成したUpdateStateProxyMessageをもとに指定されたClient IDに対応するLCP Clientの状態遷移を行う。この関数は、UpdateClient関数により呼び出される。
関数は次のように定義される:
struct UpdateStateProxyMessage {
Height prevHeight;
bytes32 prevStateId;
Height postHeight;
bytes32 postStateId;
uint128 timestamp;
bytes context;
EmittedState[] emittedStates;
}
function updateState(string calldata clientId, UpdateStateProxyMessage memory pmsg)
internal
returns (Height[] memory heights)
{
ClientState storage clientState = STORAGE[clientId].clientState;
require(!clientState.frozen, "clientState must not be frozen");
// if the `latest_height` is zero, the client is not initialized
if (clientState.latest_height.revision_number == 0 && clientState.latest_height.revision_height == 0) {
// if the client is not initialized, `emittedStates` must not be empty
// This is because the initial state must be always available for the LCP recovery process: ../06-security-model.md#state-recovery-protocol
require(pmsg.emittedStates.length > 0, "emittedStates must not be empty");
} else {
require(pmsg.prevStateId != bytes32(0), "prevStateId must not be empty");
require(STORAGE[clientId].consensusStates[pmsg.prevHeight.toUint128()].stateId == pmsg.prevStateId, "unexpected prevStateId");
}
// check if the `UpdateStateCommitment` is valid with the chain's latest block timestamp
validateContext(pmsg.context, block.timestamp * 1e9);
uint128 latestHeight = clientState.latest_height.toUint128();
uint128 postHeight = pmsg.postHeight.toUint128();
if (latestHeight < postHeight) {
clientState.latest_height = pmsg.postHeight;
}
ConsensusState storage consensusState = STORAGE[clientId].consensusStates[postHeight];
consensusState.stateId = pmsg.postStateId;
consensusState.timestamp = uint64(pmsg.timestamp);
return [pmsg.postHeight];
}
この関数は、次のような検証を行う:
clientIdに対応するClientStateが凍結されていないことlatest_heightが0である場合、emitted_statesが空でないことlatest_heightが0の場合、ClientStateは初期化が完了していないことを示す。最初のupdateStateのcommitmentにはemitted_statesが含まれる必要がある。この理由は、LCPのState Recovery Protocolのためであり、
latest_heightが0でない場合、prev_state_idが空でないことprev_state_idがprev_heightに対応するConsensusStateのstate_idと一致すること
contextのValidation Contextがchainの最新のblock timestampを基準として有効であること
最初のupdateStateのcommitmentにはemitted_statesが含まれる必要があり、この理由は、LCPのState Recovery Protocolのためである。
また、検証に成功した場合、post_heightがlatest_heightより大きい場合、ClientStateのlatest_heightをpost_heightに更新し、post_heightをconsensus heightとしてpost_state_idとtimestampを元にConsensusStateを作成する。
SubmitMisbehaviour
この関数は、MisbehaviourProxyMessageを検証し、ClientStateを凍結する。この関数は、UpdateClient関数により呼び出される。
struct MisbehaviourProxyMessage {
PrevState[] prevStates;
bytes context;
bytes clientMessage;
}
struct PrevState {
Height height;
bytes32 stateId;
}
function submitMisbehaviour(string calldata clientId, MisbehaviourProxyMessage memory pmsg)
internal
returns (Height memory heights)
{
require(!STORAGE[clientId].clientState.frozen, "clientState must not be frozen");
require(pmsg.prevStates.length != 0, "prevStates must not be empty");
for (uint256 i = 0; i < pmsg.prevStates.length; i++) {
PrevState memory prev = pmsg.prevStates[i];
require(prev.stateId != bytes32(0), "prevStateId must not be empty");
require(STORAGE[clientId].consensusStates[prev.height].stateId == prev.stateId, "unexpected prevStateId");
}
validateContext(pmsg.context, block.timestamp * 1e9);
STORAGE[clientId].clientState.frozen = true;
return heights;
}
この関数は、次のような検証を行う:
clientIdに対応するclientStateが凍結されていないことprevStatesが空でないことprevStatesの各要素prev_stateに対して、prev_state.heightに対応するConsensusStateが存在し、そのstateIdがprev_state.stateIdと一致すること
また、検証に成功した場合、ClientStateのfrozenをtrueに更新する。
VerifyMembership
verifyMembershipおよびverifyNonMembership関数は、Clientが保持するConsensusStateに基づいて、ELCのVerifyMembershipCommitmentを検証する。
struct CommitmentProofs {
/// @dev message is `VerifyMembershipProxyMessage` or `VerifyNonMembershipProxyMessage` serialized to bytes
bytes message;
/// @dev signatures are the EK signatures
bytes[] signatures;
}
function verifyMembership(
string calldata clientId,
Height.Data calldata height,
uint64,
uint64,
bytes calldata proof,
bytes calldata prefix,
bytes calldata path,
bytes calldata value
) public view returns (bool) {
(
CommitmentProofs memory commitmentProofs,
VerifyMembershipProxyMessage memory message
) = decode(proof);
validateProxyMessage(STORAGE[clientId], message, height, prefix, path);
require(keccak256(value) == message.value, "invalid value");
verifySignatures(clientId, keccak256(commitmentProofs.message), commitmentProofs.signatures)
return true;
}
function verifyNonMembership(
string calldata clientId,
Height.Data calldata height,
uint64,
uint64,
bytes calldata proof,
bytes calldata prefix,
bytes calldata path
) public view returns (bool) {
(
CommitmentProofs memory commitmentProofs,
VerifyMembershipProxyMessage memory message
) = decode(proof);
validateProxyMessage(STORAGE[clientId], message, height, prefix, path);
require(message.value.length == 0, "invalid value");
verifySignatures(clientId, keccak256(commitmentProofs.message), commitmentProofs.signatures)
return true;
}
function validateProxyMessage(
string calldata clientId,
VerifyMembershipProxyMessage memory message,
Height calldata height,
bytes calldata prefix,
bytes calldata path
) internal view {
ConsensusState storage consensusState = clientStorage.consensusStates[message.height];
require(consensusState.stateId != bytes32(0), "consensus state not found");
require(height == messageHeight, "invalid height");
require(keccak256(prefix) == keccak256(message.prefix), "invalid prefix");
require(keccak256(path) == keccak256(message.path), "invalid path");
require(consensusState.stateId == message.stateId, "invalid stateId");
}
これらの関数は、次のような検証を行う:
message.prefixが与えられたprefixと一致することmessage.pathが与えられたpathと一致することmessage.heightに対応するConsensusStateが存在し、そのstateIdがmessage.stateIdと一致することverifyMembershipの場合、message.valueが検証対象の値と一致することverifyNonMembershipの場合、message.valueが空であること
なお、clientIdに対応するClientStateが凍結されていないことは呼び出し元で検証されなければならないことに注意する。
UpdateOperators
UpdateOperators関数は、ClientIDに対応するClientのOperatorの追加、削除、および閾値の変更を行う。
この関数は、CreateClient関数による初期化時にoperatorsが空の場合は失敗する。
struct UpdateOperatorsMessage {
uint64 nonce;
bytes[] new_operators;
uint64 new_operators_threshold_numerator;
uint64 new_operators_threshold_denominator;
bytes[] signatures;
}
function updateOperators(string calldata clientId, UpdateOperatorsMessage calldata message)
public
returns (Height[] memory heights)
{
ClientState.Data storage clientState = STORAGE[clientId].clientState;
require(clientState.operators.length > 0, "permissionless client cannot update operators");
require(message.signatures.length == clientState.operators.length, "invalid signatures length");
require(
message.new_operators_threshold_numerator != 0 && message.new_operators_threshold_denominator != 0,
"invalid operators threshold"
);
uint64 nextNonce = clientState.operators_nonce + 1;
require(message.nonce == nextNonce, "unexpected operators nonce");
bytes32 commitment = keccak256(
computeEIP712UpdateOperators(
clientId,
nextNonce,
message.new_operators,
message.new_operators_threshold_numerator,
message.new_operators_threshold_denominator
)
);
uint256 success = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < message.signatures.length; i++) {
if (message.signatures[i].length > 0) {
address operator = verifyECDSASignature(commitment, message.signatures[i]);
require(operator == address(bytes20(clientState.operators[i])), "unexpected operator");
success++;
}
}
require(success * STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators_threshold_denominator >=
STORAGE[clientId].clientState.operators_threshold_numerator * clientState.operators.length,
"insufficient signatures");
// delete the previous operators
delete clientState.operators;
// ensure the new operators are sorted(ascending order) and unique
for (uint256 i = 0; i < newOperators.length; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
require(newOperators[i - 1] < newOperators[i], "invalid operator address order");
}
clientState.operators.push(message.new_operators[i]);
}
clientState.operators_nonce = nextNonce;
clientState.operators_threshold_numerator = message.new_operators_threshold_numerator;
clientState.operators_threshold_denominator = message.new_operators_threshold_denominator;
return heights;
}
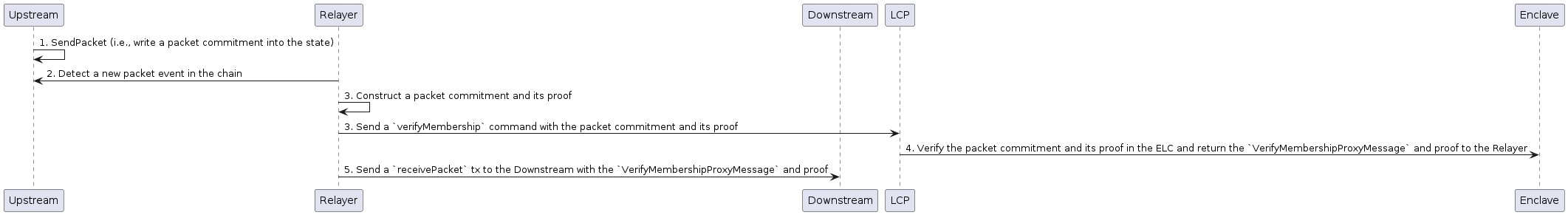
Communication Flow
LCP Clientと他の関連コンポーネントの間の通信フローを示す。
Initialization
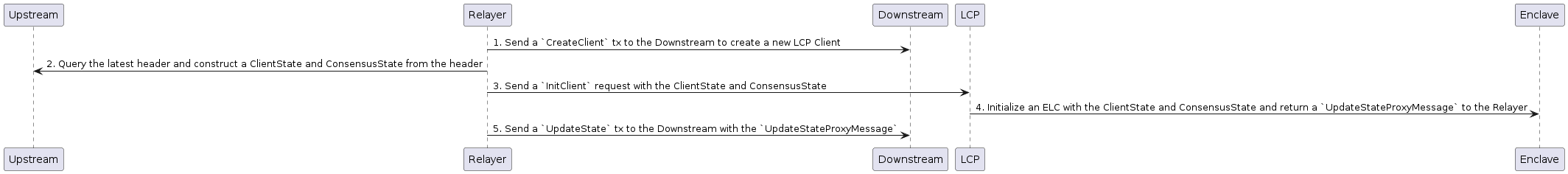
Register EK
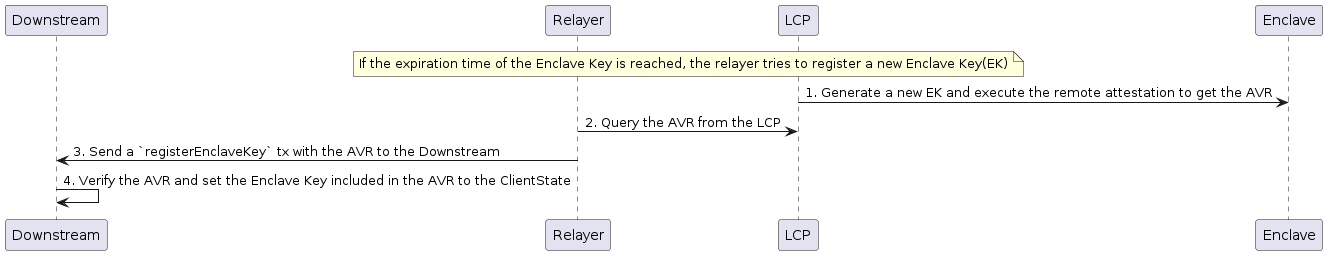
Packet-relay flow