Architecture
Overview
The LCP works with the IBC Relayer, which relays messages and packets transmitted between two blockchains. Since the receiving chain does not directly perform light client verification, the relayer requests the LCP to verify the source chain. The Relayer then submits the verification results to the destination chain, which verifies it.
The following figure shows the architecture and packet-relay flow between the two chains using the LCP.
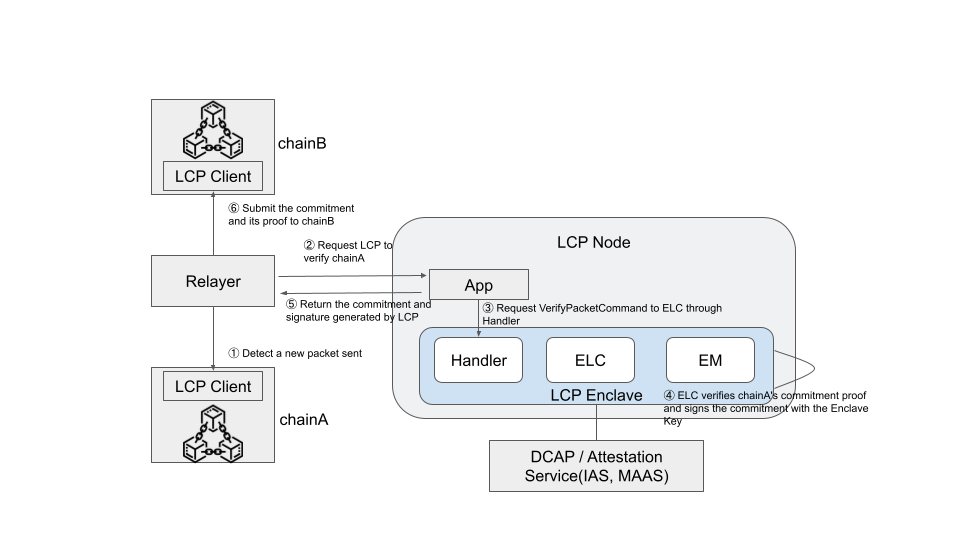
Each step of the packet-relay process is described below. This example assumes that chain B verifies the packet proof from chain A.
- First, a relayer detects that a packet has been sent from chain A to chain B.
- The relayer requests the LCP Node's App to verify chain A.
- The App sends a
VerifyMembershipcommand to the LCP Enclave to verify the packet. The handler processes the command and requests the ELC to verify the packet. - The ELC verifies the packet commitment using the Light Client corresponding to chain A and signs the commitment with the Enclave Key to generate proof.
- The Enclave returns the commitment and proof from step 4, and the App sends them back to the relayer.
- The relayer submits the commitment and proof to chain B, where the LCP Client verifies them using the EKPub.
Components
LCP Node
The LCP Node is equipped with Intel SGX and executes the Host Application and the LCP Enclave.
Host Application
The Host Application (also called App) is responsible for creating the LCP Enclave, generating the Enclave Key (EK), and requesting verification from the ELC based on the relayer’s requests. It also implements a GRPC server for these interactions.
The App interacts with the Architectural Enclave (AE) to create a Quote containing the LCP Enclave information for Remote Attestation. By sending this Quote to an Attestation Service, such as IAS, a Verifiable Quote can be obtained. If using DCAP (ECDSA attestation), the Quote can be verified directly by an external verifier without using IAS.
LCP Enclave
The LCP Enclave (also called Enclave) consists of the Handler, Enclave Manager (EM), and ELC modules. The ELC module can be registered in the Enclave using register_implementation, and multiple ELCs can be registered in a single Enclave.
The Handler routes requests from the Host App (via ecall) to the appropriate modules for execution.
Enclave Light Client (ELC)
ELC is a Light Client module that runs within the Enclave.
ELC verifies the headers and existence proofs of the chain requested by the relayer (through the App) and generates a new commitment based on the results. It signs the commitment with the Enclave Key to generate a proof and returns both the commitment and proof to the App. The relayer, upon receiving these, submits them to the target chain, where they are verified by the LCP Client.
See here for detail.
Enclave Manager (EM)
EM generates theEK used to sign commitments and create proofs for ELC. It also generates the Report containing the public Enclave Key required for Remote Attestation, allowing external verifiers to validate the integrity of the Enclave.
Attestation Service
Attestation Service is a service that provides remote attestation to enable remote parties to validate enclaves. IAS and Microsoft Azure Attestation (MAA) are such examples. ECDSA attestation is a method that does not require an external service. LCP initially supports IAS. In this document, Remote Attestation refers to IAS unless otherwise noted.
By verifying the signature of the Verifiable Quote obtained from the Attestation Service and comparing it against the expected MRENCLAVE value, verifiers can confirm that the data in the Quote was constructed by the correct Enclave. This process also verifies that the EK was properly generated within the Enclave. Details of this process are explained in Remote Attestation.
Relayer
The Relayer acts as an intermediary between two chains, providing necessary data to the verifying chain and interacting with the LCP Node. It functions similarly to the relayer in IBC.
LCP Client
The LCP Client is an IBC client implementation that verifies the commitments and proofs generated by the ELC. The LCP Client verifies the Verifiable Quote created by the Attestation Service for the LCP Enclave, retrieves and stores the Enclave Key, and uses this key to verify the commitments generated by the ELC, thereby ensuring the validity of the upstream chain's state transition and membership proofs.
See here for detail.